简单理解容器是个什么鬼¶
镜像(image),是一个独立、轻量级的可运行包。它包含了运行一个软件所需要的代码、运行环境、依赖库、环境变量、配置文件等其它必须的东西。
容器(container),是一个镜像的运行实例,也就是镜像运行时被加载到了内存中。默认情况下,容器运行可以做到和宿主机完全互不影响。当然,如果明确配置了交互的情况下,容器也可以访问宿主机的文件和端口。
容器是基于宿主机的内核来运行应用程序的。它比仅通过hypervisor访问宿主机资源的虚拟机有更高的执行效率。因为容器可以作为宿主机的一个进程运行,所以更加节约内存资源。
窗口 VS 虚拟机¶
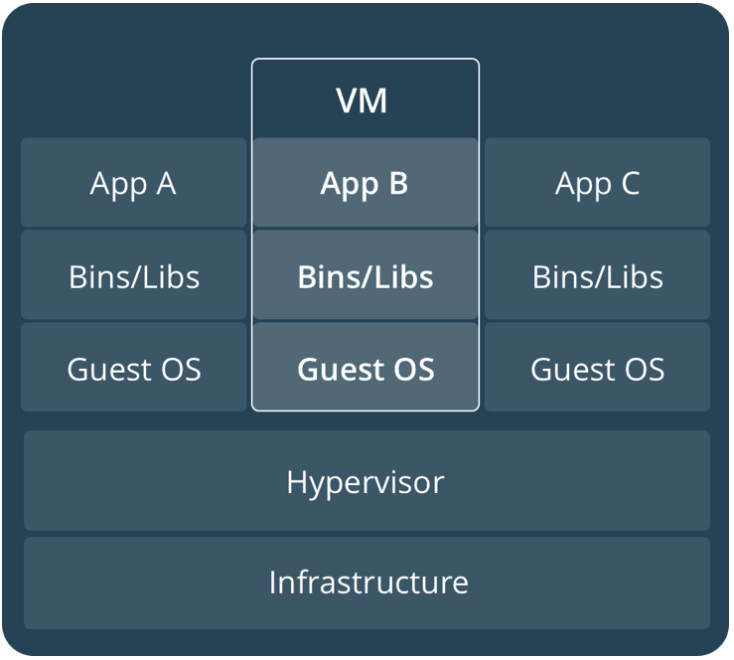
虚拟机会运行Guest OS,这是很耗费资源的,并且这个Guest OS的磁盘镜像和应用状态很容易纠缠在一起。并且每一个Guest OS的系统设置、系统依赖、系统安全补丁和一些其它细节很难保证一致。
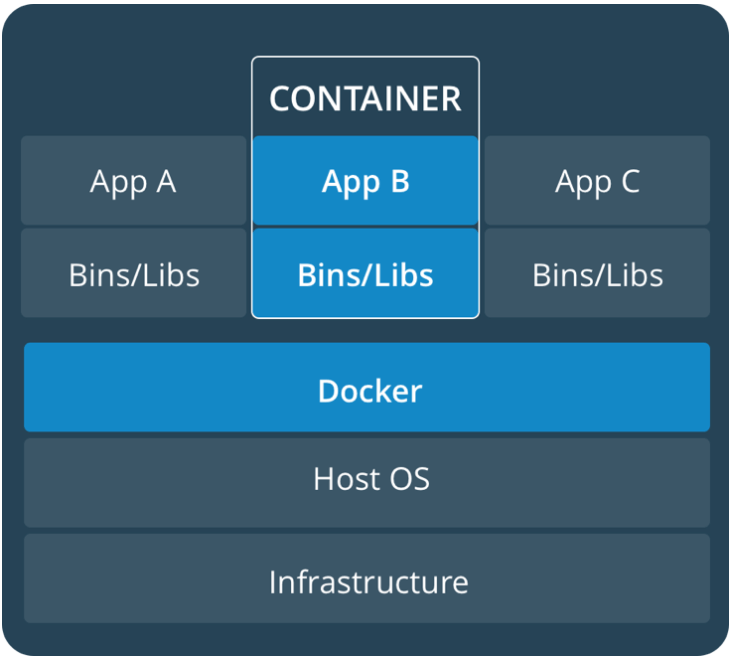
容器可以共享内核,并且容器镜像内唯一需要的信息就是所要执行的文件和它的依赖,而这些信息是不需要安装在操作系统上的。这使得容器可以像本地进程一样运行和管理。你可以像在linux上使用ps命令一样,使用docker ps来查看活动容器的运行情况,因为容器内包含了所有运行所需要的依赖,所以它们之间的配置不会纠缠在一起,可以在任何地方运行。
安装Docker¶
先要确保你安装了最版本的docker,版本在1.13之后。
安装完成后,测试一下安装是否正确, 并确认一下你的docker版本:
$ docker run hello-world && docker --version
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
b04784fba78d: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:f3b3b28a45160805bb16542c9531888519430e9e6d6ffc09d72261b0d26ff74f
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://cloud.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/engine/userguide/
Docker version 17.06.0-ce, build 02c1d87
小结¶
扩展单元的独立性、移植性意味着持续集成和持续分发可以随时更新应用的相关部分,避免了系统依赖并且增大了资源利用率。扩展行为的编排只和新的应用用关,而与主机无关。